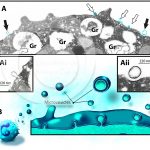
 Ultrastructural changes during the ETosis process of human eosinophils in vivo
Ultrastructural changes during the ETosis process of human eosinophils in vivo
–
NEVES, V. H. et al. (2022) In Vivo ETosis of Human Eosinophils: The Ultrastructural Signature Captured by TEM in Eosinophilic Diseases. Front Immunol.
–
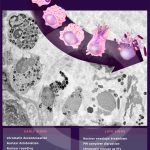
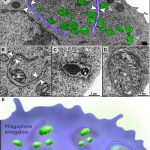 Mitophagy events in immature eosinophils
Mitophagy events in immature eosinophils
–
BONJOUR, K. et al. (2022) Mitochondrial Population in Mouse Eosinophils: Ultrastructural Dynamics in Cell Differentiation and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol.
–
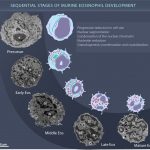 Stages of eosinophil development observed by Transmission Electron Microscopy
Stages of eosinophil development observed by Transmission Electron Microscopy
–
BONJOUR, K. et al. (2022) Mitochondrial Population in Mouse Eosinophils: Ultrastructural Dynamics in Cell Differentiation and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol.
–
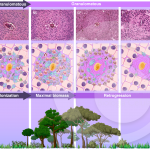 Ecological succession in Schistosoma mansoni hepatic granuloma
Ecological succession in Schistosoma mansoni hepatic granuloma
–
MALTA, K. K. et al. (2021) Changing our view of the Schistosoma granuloma to an ecological standpoint. Biol Rev.
–
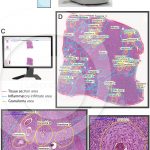 Whole slide imaging of granulomas in a section of liver infected with Schistosoma mansoni
Whole slide imaging of granulomas in a section of liver infected with Schistosoma mansoni
–
MELO, R. C. N. et al. (2020) Whole slide imaging and its applications to histopathological studies of liver disorders. Front Med.
–
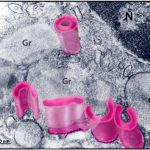 Morphology of the secretory vesicles of human eosinophils (Eosinophil Sombrero Vesicles)
Morphology of the secretory vesicles of human eosinophils (Eosinophil Sombrero Vesicles)
–
CARMO, L. A. S. et al. (2018) Single-Cell Analyses of Human Eosinophils at High Resolution to Understand Compartmentalization and Vesicular Trafficking of Interferon-Gamma. Front Immunol.
–
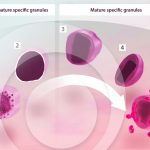 Stages of human eosinophil secretory granule development
Stages of human eosinophil secretory granule development
–
MELO, R. C. N.; WELLER, P. F. (2018). Contemporary understanding of the secretory granules in human eosinophils. J Leukoc Biol.
–
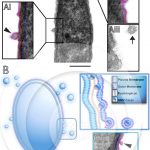 Release of external membrane vesicles by bacteria from aquatic ecosystems
Release of external membrane vesicles by bacteria from aquatic ecosystems
–
GAMALIER, J. P. et al. (2017). Increased production of outer membrane vesicles by cultured freshwater bacteria in response to ultraviolet radiation. Microbiol Res.
–
Release of microvesicles by human eosinophil activated by inflammatory stimuli
–
AKUTHOTA, P. et al. (2016). Extracellular Microvesicle Production by Human Eosinophils Activated by “Inflammatory” Stimuli. Front Cell Dev Biol.
–
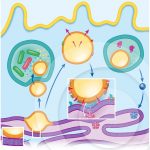 A model that explains the role of lipid bodies during infections with different intracellular pathogens
A model that explains the role of lipid bodies during infections with different intracellular pathogens
–
ROINGEARD, P.; MELO, R. C. N. (2016). Lipid droplet hijacking by intracellular pathogens. Cell Microbiol.
–
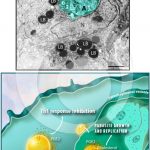 Lipid bodies accumulate in the host cell cytoplasm in response to interaction with protozoan parasites and favor parasite survival
Lipid bodies accumulate in the host cell cytoplasm in response to interaction with protozoan parasites and favor parasite survival
–
TOLEDO, D. A. et al. (2016). Host Lipid Bodies as Platforms for Intracellular Survival of Protozoan Parasites. Front Immunol.
–—
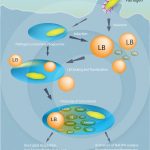 Formation of lipid bodies induced by various pathogens
Formation of lipid bodies induced by various pathogens
–
DIAS, F. F. et al. (2014). The Intriguing Ultrastructure of Lipid Body Organelles Within Activated Macrophages. Microsc Microanal.
–
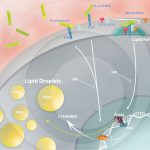 Increased PPARγ expression and lipid accumulation during M. bovis BCG infection
Increased PPARγ expression and lipid accumulation during M. bovis BCG infection
–
ALMEIDA, P. E. et. al. (2014). Differential TLR2 downstream signaling regulates lipid metabolism and 2 cytokine production triggered by Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta.
–
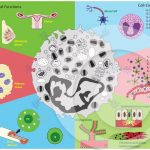 Biological effects of eosinophil-derived cytokines in health and disease
Biological effects of eosinophil-derived cytokines in health and disease
–
MELO, R. C. N. et al. (2013). Eosinophil-derived cytokines in health and disease: unraveling novel mechanisms of selective secretion. Allergy.
–
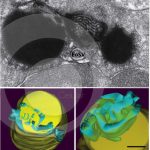 Three-dimensional (3D) architecture of lipid bodies in human eosinophils
Three-dimensional (3D) architecture of lipid bodies in human eosinophils
–
MELO, R. C. N. et al. (2013). The internal architecture of leukocyte lipid body organelles captured by three-dimensional electron microscopy tomography. Plos One.
–
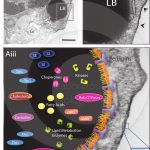 Lipid bodies, structure and composition
Lipid bodies, structure and composition
–
MELO, R. C. N; DVORAK, A. M. (2012). Lipid Body–Phagosome Interaction in Macrophages during Infectious Diseases: Host Defense or Pathogen Survival Strategy? PLoS Pathog.
–
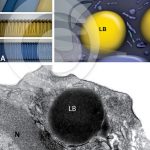 Comparison between the lipid body membrane and the plasma membrane
Comparison between the lipid body membrane and the plasma membrane
–
MELO, R. C. N. et al. (2011). Lipid bodies in inflammatory cells: structure, function, and current imaging techniques. J Histochem Cytochem.
–
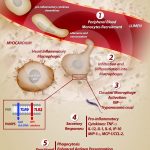 Activation of inflammatory heart macrophages during acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection
Activation of inflammatory heart macrophages during acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection
–
MELO, R. C. N. (2009). Acute heart inflammation: ultrastructural and functional aspects of macrophages elicited by Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Cell Mol Med.
–
–